
Long Island Allergy Testing
Long Island Allergy Testing is a part of the Heart and Health Medical Network and has four locations; Massapequa, Coram, North Babylon, and Plainview. Current and New Patients have convenient access to Allergy Testing & Treatment as well as the latest advancements in short and long-term care. The Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology Team is led by renowned award-winning Allergist & Immunologist Dr. Luis Guida Jr. with 36 years of experience he is one of the most recognized medical authorities of Allergy & Immunology care in Long Island. The team at Heart and Health Allergy & Immunology will provide the most advanced Allergy Testing available as well as custom treatment plans for each patient.

Accepted Insurances















Understanding Allergies & Allergens
Allergy tests are exams performed by trained allergy specialists to determine if your body has an allergic reaction to a known substance. The exam can be in the form of a blood test, a skin test, or an elimination diet. Allergies occur when your immune system, which is your body’s natural defense, overreacts to something in your environment, called an “Allergen”. For example, pollen, which is normally harmless, can cause your body to overreact and is a potential “Allergen”.
Common Allergy symptoms:
- Runny nose
- Sneezing
- Blocked sinuses
- Itchy, watery eyes

Understanding the Three Primary Types of Allergens
Allergens, substances that can cause allergic reactions, are typically categorized into three primary types based on their mode of interaction with the body:
Inhaled Allergens: These allergens affect the body when they are inhaled into the lungs or come into contact with the membranes of the nostrils or throat. The most common example of an inhaled allergen is pollen, often responsible for seasonal allergies.
Ingested Allergens: This category includes allergens present in certain foods. Common ingested allergens are found in foods like peanuts, soy, and seafood, which can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Contact Allergens: These allergens must directly touch the skin to provoke an allergic response. A typical reaction to a contact allergen is the rash and itching caused by poison ivy, which occurs upon skin contact with the plant.
Understanding these types of allergens is crucial in identifying and managing allergic reactions effectively. Recognizing the source of an allergen can help in adopting appropriate preventive measures and treatments.
Inhaled Allergens: Understanding Seasonal and Year-Round Triggers
Inhaled allergies represent the most common form of allergic reactions. Many individuals with these allergies experience symptoms primarily during specific times of the year. Common symptoms include sneezing, a runny nose, watery eyes, and itchy eyes. Pollen, grass, and mold are typical triggers for these seasonal allergies.
Pollen, a fine powdery substance produced by trees, weeds, and grasses, becomes more prevalent in the air from spring through fall. The increased levels of pollen during these seasons can trigger allergic reactions in people who are sensitive to it.
However, avoiding pollen is not always a straightforward task, especially since allergens aren’t confined to outdoor environments. Indoors, other types of airborne allergens can be just as prevalent. These include fungi, mold, pet dander, and dust mites. Being aware of these indoor allergens is crucial, as they can cause year-round allergy symptoms and significantly impact daily life.
To effectively manage inhaled allergies, it’s essential to understand both outdoor and indoor allergens and to adopt appropriate strategies for minimizing exposure and alleviating symptoms.
Ingested Allergens: Recognizing and Managing Food Allergies
Food allergies, a type of food intolerance, involve an abnormal immune reaction to certain foods, also known as food hypersensitivity. These allergies are more prevalent in children than adults and can be triggered by various foods, including cow’s milk, nuts, eggs, and some fruits.
When a person with a food allergy consumes the triggering food, their immune system overreacts. Most individuals with food allergies have elevated levels of food-specific immunoglobulin IgE in their bloodstream. These antibodies bind to the allergen and then to mast cells in the skin, causing the release of histamine. Histamine release leads to hives — red, itchy, and inflamed skin.
While symptoms like hives can be mild, food allergies can also manifest in more severe forms, including:
- Abdominal cramps
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Skin rash
- Rapid swelling of the lips and eyes
- Anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction marked by difficulty breathing, swelling of the tongue or throat, and in extreme cases, death
It’s important to note that any food allergy has the potential to escalate to anaphylaxis, regardless of the severity of previous reactions. In children, food allergies may also present as behavioral changes such as crying, irritability, or refusal to consume certain foods like milk.
Understanding the range of symptoms associated with food allergies is vital for early recognition and effective management. Immediate medical attention is crucial for severe reactions, especially anaphylaxis, to prevent life-threatening complications.
Understanding Contact Allergies: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Contact allergies arise when an allergen comes into direct contact with the skin, typically triggering symptoms in the affected area. Common sources of contact allergens include everyday substances like soaps, detergents, hair dyes, certain types of jewelry, solvents, waxes, polishes, and plants like ragweed.
While contact allergies can cause considerable discomfort, they are generally not life-threatening. The typical symptoms of a contact allergy include skin redness, itching, swelling, scaling, and sometimes blistering. These reactions are usually localized to the area of skin that came in contact with the allergen.
The primary strategy for managing contact allergies is to identify and avoid the offending irritant. Treatment options can include topical creams or ointments to soothe the symptoms, antihistamines to prevent allergic reactions, and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and discomfort.
With appropriate treatment, the symptoms of contact allergies typically resolve within a few days. However, it’s important to consult a doctor if the rash exhibits signs of infection, such as drainage accompanied by pain or fever, or if red streaks appear spreading from the rash. These symptoms could indicate an infection rather than a simple allergic reaction.
Patient Reviews
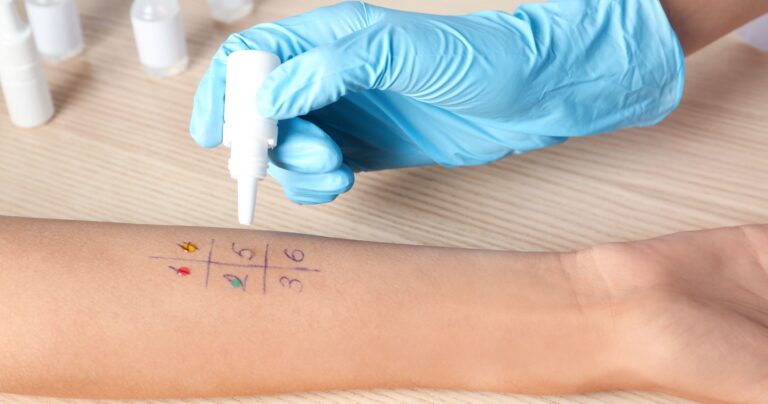
Skin Tests
Skin tests are used to identify numerous potential allergens. This includes airborne, food-related, and contact allergens. The three types of skin tests are:
Scratch Test: an allergen is placed in liquid, then that liquid is placed on a section of your skin with a special tool that lightly punctures the allergen into the skin’s surface. You’ll be closely monitored to see how your skin reacts to the foreign substance. If there is localized redness, swelling, elevation, or itchiness of the skin over the test site, you’re allergic to that specific allergen.
Intradermal Test: This test requires injecting a tiny amount of allergen into the dermis layer of your skin. Again, your doctor will monitor your reaction.
Patch Test: This involves using adhesive patches loaded with suspected allergens and placing these patches on your skin. The patches will remain on your body after you leave your doctor’s office. The patches are then reviewed 48 hours after application and again at 72 to 96 hours after application.
Blood tests
If there’s a chance you’ll have a severe allergic reaction to a skin test, your doctor may call for a blood test. The blood is tested in a laboratory for the presence of antibodies that fight specific allergens. This test is very successful in detecting IgE antibodies to major allergens.
Elimination diet
An elimination diet may help your doctor determine which foods are causing you to have an allergic reaction. It entails removing certain foods from your diet and later adding them back in. Your reactions will help determine which foods cause problems.
Medical Grade Allergy Testing vs At Home Testing
Allergy tests may help find allergies to things you eat, touch, or breathe in. They are usually skin or blood tests. However, allergy tests are not all created equal and alone are generally not enough. It is important to have a doctor’s exam and medical history first to help diagnose allergies.
Allergy tests, without a doctor’s exam, usually are not reliable.
Many drugstores and supermarkets offer free screenings. And you can even buy kits to test for allergies yourself at home. But the results of these tests may be misleading and are often unreliable creating further problems.
- The tests may say you have an allergy when you do not. This is called a “false positive.”
- These free tests and home tests for food allergies are not always reliable.
If the test says you are allergic to some foods, such as wheat, soy, eggs, or milk, you may stop eating those foods. You may end up with a poor diet, unnecessary worries and frustration, or extra food costs. If the test says you are allergic to cats or dogs, you may give up a loved pet. And tests for chronic hives—red, itchy, raised areas of the skin that last for more than six weeks—can show something that may not look normal but is not a problem. However, this can lead to anxiety, more tests, and referrals to specialists.
Hospital Affiliations






Find An Allergy Testing Office Near You
Coram: 3650 Route 112, Coram, NY 11727
Levittown: 1 Center Lane, Levittown 11756
Massapequa: 6175 Sunrise Highway, Massapequa, NY 11758
North Babylon: 1350 Deer Park Avenue, North Babylon, NY 11703
Plainview: 1070 Old Country Road, Plainview NY 11803
